
LP Expectations for GPs’ Sustainability Strategies
LPs are a significant driving force behind the adoption of ESG in private markets. But how can GPs ensure they are meeting



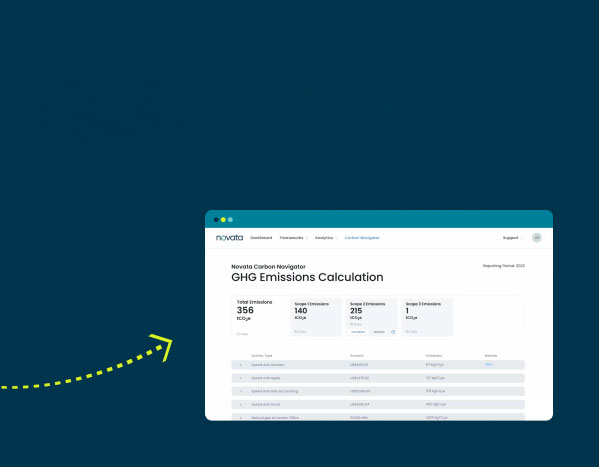

At Novata, we dive deep into CSRD and its requirements to help you simplify and optimize your implementation processes. Our suite of expert services, paired with our leading ESG data management platform, remove the operational burdens and uncertainties associated with CSRD and position you for success in your CSRD initiatives.
Novata’s suite of expert services, paired with our leading ESG data management platform, removes the operational burdens and uncertainties associated with the CSRD and positions you for success in your CSRD initiatives.

Educate your workforce, understand the level of effort required, and set your company up for success.
Available Q3 2024
Complete your Double Materiality Assessment (DMA) to figure out what matters to your company and value chain through two lenses: environmental and social impact, and financial.
Start collecting ESRS data, gathering evidence, and setting goals.
Reflect on your progress to date and identify areas to improve ahead of the full data collection process.

Available Q4 2024
Share what you’re doing and make sure it’s accurate with our reporting and assurance tools.
The aim of the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) is to help key stakeholders, such as investors, consumers, and suppliers, better evaluate the sustainability performance of companies through a reliable and standardized way of reporting and, in turn, reorient capital to sustainable investments.
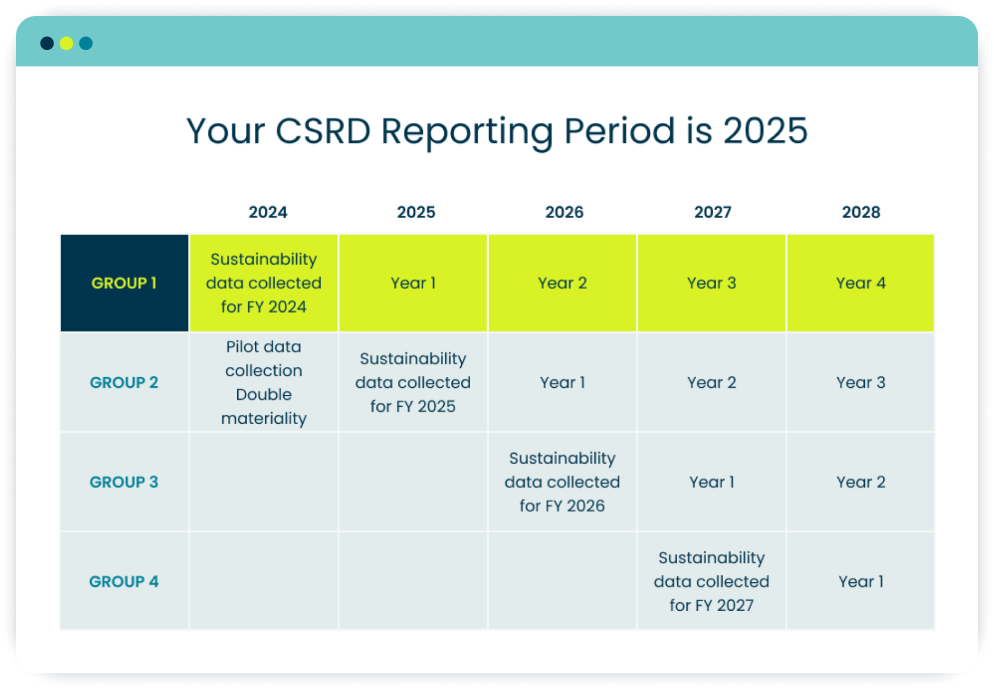
Companies will become mandated iteratively over time from 2024 to 2029 depending on location, size, and financials. Some examples include the revenue, turnover, or number of employees.
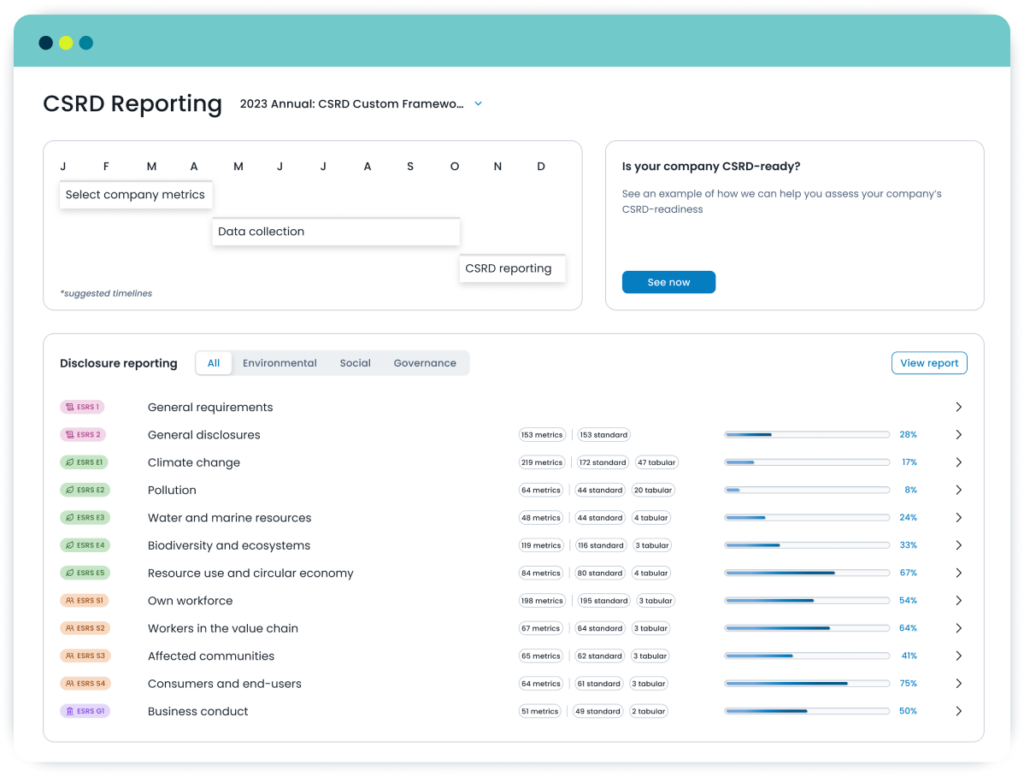
There are no “CSRD metrics.” Instead, the EU developed European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). These are the instructions companies must follow to comply with CSRD. There are two different sets of ESRS: ESRS 1 (“General Requirements”) which set the general principles to be applied and do not set specific disclosure requirements; and ESRS 2 (“General Disclosures”) which specify essential information to be disclosed irrespective of the sustainability matter being considered.

LPs are a significant driving force behind the adoption of ESG in private markets. But how can GPs ensure they are meeting

There is a rising focus on ESG regulations in the US market, characterized by increasing investor pressures and a growing understanding of

Identifying the ESG metrics that matter to stakeholders is foundational to a company’s ESG journey. The Novata ESG Metrics Guide provides visibility